Chemical Bonding — Basic Concepts: Draw Lewis Structures and Calculate Formal Charge
You may choose to prevent this website from aggregating and analyzing the actions you take here. Doing so will protect your privacy, but will also prevent the owner from learning from your actions and creating a better experience for you and other users.
This opt out feature requires JavaScript.
Question
Iodine forms a series of fluorides. Draw Lewis structures for each of the 4 compounds listed below and determine the formal charge of the iodine atom in each molecule:
- IF
- IF3
- IF5
- IF7
Show/Hide Answer
Lewis Structures:
Formal Charges on I:
- IF — formal charge on I = 0
- IF3 — formal charge on I = 0
- IF5 — formal charge on I = 0
- IF7 — formal charge on I = 0
Refer to:
Strategy Map
Do you need a little help to get started?
Check out the strategy map.
Show/Hide Strategy Map
| Strategy Map Steps |
|---|
1. Count valence electrons in the molecule.
Show/Hide HintValence electrons are the outer shell electrons. |
2. Draw the Lewis structures.
Show/Hide HintTo recall the step for drawing a Lewis structure, refer to Section 4.4: Lewis Symbols and Structures (1). Show/Hide Steps
|
3. Calculate the formal charge.
Show/Hide HintTo recall the steps for calculating formal charge, refer to Section 4.5: Formal Charges and Resonance (2). Show/Hide Steps
|
Solution
Do you want to see the steps to reach the answer?
Check out this solution.
Show/Hide Solution
a. IF
Lewis Structure:
(1) Iodine + (1) Fluorine
7ve– + 7ve– = 14e–

| Element | Iodine |
|---|---|
| Valence Electrons | 7 |
| Assigned Electrons | 7 |
| Formal Charges | 0 |
b. IF3
Lewis Structure:
(1) Iodine + (3) Fluorine
7ve– + (3)7ve– = 28e–
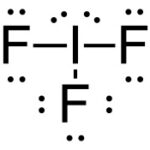
| Element | Iodine |
|---|---|
| Valence Electrons | 7 |
| Assigned Electrons | 7 |
| Formal Charges | 0 |
c. IF5
Lewis Structure:
(1) Iodine + (5) Fluorine
7ve– + (5)7ve– = 42e–
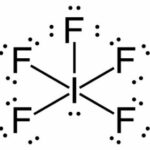
| Element | Iodine |
|---|---|
| Valence Electrons | 7 |
| Assigned Electrons | 7 |
| Formal Charges | 0 |
d. IF7Lewis Structure:
(1) Iodine + (7) Fluorine
7ve– + (7)7ve– = 56e–
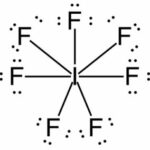
| Element | Iodine |
|---|---|
| Valence Electrons | 7 |
| Assigned Electrons | 7 |
| Formal Charges | 0 |
Guided Solution
Do you want more help?
The guided solution below will give you the reasoning for each step to get your answer, with reminders and hints.
Show/Hide Guided Solution
| Guided Solution Ideas | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This question is a Lewis structure application problem. In this problem, you must follow the steps to create 4 different Lewis structures and find their corresponding formal charges on I.
Show/Hide Resource
|
||||||||||||
| Note: The Guided Solution detailed below is for question 2 (IF3) only.
To work through creating Lewis structures and calculating formal charges for all species, check out the following interactive video: If you are using a printed copy, you can scan the QR code with your digital device to go directly to the h5p:
|
||||||||||||
Count valence electrons in the molecule by identifying what atoms there are, counting the valence electrons each has, and adding them.
Show/Hide Don’t ForgetTo find how many valence electrons an atom has, count across the periodic table (skipping the d-block elements). You can use the group number or electron configuration to find the number of valence electrons in each type of atom.
You cannot have more electrons in a molecule than the amount each of the atoms has combined. For example, since iodine has 7 valence electrons and fluorine has 7 valence electrons, the total number of electrons in the structure of IF will be 14. |
||||||||||||
Draw the Lewis structure.
Show/Hide Steps
Check that you followed the octet rule and that the total number of electrons you used (either as a dot/lone pair or in a line) add up to the total amount you counted in the beginning. |
||||||||||||
Calculate formal charge:
It can be useful to track valence electrons and calculate formal charges using a table, as shown below, especially if you are working with many atoms. Show/Hide Table Template
|
| Complete Solution for b. IF3 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Count valence electrons:
Show/Hide Don’t Forget!(amount of Iodine atoms)x7ve– + (amount of Fluorine atoms)x7ve– = total valence electrons |
||||||||
Draw Lewis Structure:
Show/Hide Think About This!Now, each F atom has a complete octet, so the octet rule is satisfied. We can have an expanded octet since it is in period 5. Show/Hide Complete Lewis Structure
|
||||||||
Formal Charge:
Show/Hide Think About This!Looking back at the Lewis structure assign 1 electron to I from the single bond, and count up all the electrons in the lone pairs on I.
Answer: The formal charge on I in IF3 is 0. |
Check Your Work
Summary of what we would expect based on the related chemistry theory.
Show/Hide Check Your Work!
The formal charge on a neutral molecule should always be 0. IF3 is neutral, so the 0 formal charge is correct.
Does your answer make chemical sense?
Show/Hide Answer
Lewis structures are a visual representation of the electrons from an atom’s outermost electron shell; they are used to illustrate when these electrions are shared in covalent bonds or present as lone pairs.
Formal charges occur when the number of electrons an atom has is different from the amount it had prior to the reaction. A formal charge can be either positive or negative. It is positive if the atom has less assigned than it originally had and negative if more are assigned. This makes sense as electrons carry a negative charge.
Formal charges can also be used to help decide which of multiple structures is preferred.
Show/Hide Resource!
Refer to Section 4.5.2: Using Formal Charges to Predict Molecular Structure (2).
Provide feedback by taking the survey here: link to survey

PASS Attribution
- LibreTexts PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500 (3).
- Question 4.E.60 from LibreTexts PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500 (4) is used under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- Question 4.E.60 was adapted from a question in Section 7.E.4: 7.5: Formal Changes and Resonance from LibreTexts Chemistry 1e (OpenSTAX) (5), which is under a CC BY 4.0 license.
- The question in Section 7.E.4: 7.5: Formal Changes and Resonance is question 60 from OpenStax Chemistry 2e (6), which is under a CC BY 4.0 license. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/chemistry-2e/pages/1-introduction.
Media Attributions
All figures by the authors (Brewer S. and Blackstock L.) are free to use under a CC0 license.
References
1. OpenStax. 4.4: Lewis Symbols and Structures. In CHEM 1500: Chemical Bonding and Organic Chemistry. LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/CHEM_1500%3A_Chemical_Bonding_and_Organic_Chemistry/04%3A_Chemical_Bonding_I-_Basic_Concepts/4.04%3A_Lewis_Symbols_and_Structures.
2. OpenStax. 4.5: Formal Charges and Resonance. In CHEM 1500: Chemical Bonding and Organic Chemistry. LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/CHEM_1500%3A_Chemical_Bonding_and_Organic_Chemistry/04%3A_Chemical_Bonding_I-_Basic_Concepts/4.05%3A_Formal_Charges_and_Resonance.
3. Blackstock, L.; Brewer, S.; Jensen, A. PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500; LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/PASS_Chemistry_Book_CHEM_1500.
4. Blackstock, L.; Brewer, S.; Jensen, A. 4.2: Question 4.E.60 PASS – Draw Lewis Structure and Calculate Formal Charge. In PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500. LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/PASS_Chemistry_Book_CHEM_1500/04%3A_Chemical_Bonding_I_-_Basic_Concepts/4.02%3A_Question_4.E.60_PASS_-_draw_Lewis_Structure_and_calculate_formal_charge.
5. OpenStax. 7.E: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry (Exercises). In Chemistry 1e (OpenSTAX). LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/General_Chemistry/Chemistry_1e_(OpenSTAX)/07%3A_Chemical_Bonding_and_Molecular_Geometry/7.E%3A_Chemical_Bonding_and_Molecular_Geometry_(Exercises).
6. Flowers, P.; Robinson, W. R.; Langley, R.; Theopold, K. Ch. 6 Exercises. In Chemistry 2e; OpenStax, 2019. https://openstax.org/books/chemistry-2e/pages/7-exercises.


