Chemical Bonding — Molecular Geometry and Hybridization: Identify Central Atom Hybridization
You may choose to prevent this website from aggregating and analyzing the actions you take here. Doing so will protect your privacy, but will also prevent the owner from learning from your actions and creating a better experience for you and other users.
This opt out feature requires JavaScript.
Question
Identify the hybridization of the central atom in each of the following molecules and ions that contain multiple bonds:
- CS2
- Cl2CO (C is the central atom)
- Cl2SO (S is the central atom)
- SO2F2 (S is the central atom)
- XeO2F2 (Xe is the central atom)
Show/Hide Answer
- sp
- sp2
- sp3
- sp3
- sp3d
Refer to Section 5.3: Hybrid Atomic Orbitals (1).
Strategy Map
Do you need a little help to get started?
Check out the strategy map.
Show/Hide Strategy Map
| Strategy Map Steps |
|---|
1. Create a Lewis structure of the molecule.
Show/Hide HintRefer to Section 4.4: Lewis Symblos and Structures (2). |
2. Determine the electron-pair geometry of the molecule.
Show/Hide HintRecall using VSEPR to determine electron-pair geometry. Refer to Section 5.1: Molecular Structure Polarity (3). |
3. Identify the hybridization of the centre atom based on the molecules’ electron-pair geometry.
Show/Hide HintThe hybridization of the centre atom will be determined by the electron-pair geometry, not the atom itself. For example, in a linear molecule, the centre atoms hybridization will always be sp. |
Solution
Do you want to see the steps to reach the answer?
Check out this solution.
Show/Hide Solution
1. CS2
16 valence electrons, C central atom
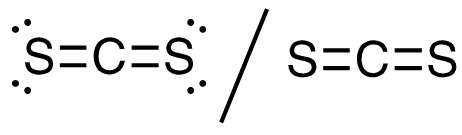
Answer: This molecule has a linear electron-pair geometry; sp hybridized (s + p)
2. Cl2CO (C is the central atom)
24 valence electrons
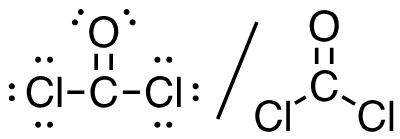
Answer: This molecule has a trigonal planar electron-pair geometry; sp2 hybridized (s + p + p)
3.Cl2SO (S is the central atom)
26 valence electrons
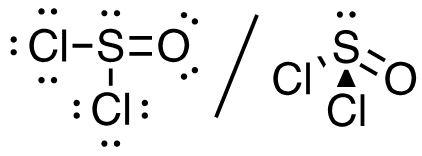
Answer: This molecule has a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry; sp3 hybridized (s + p + p + p)
4. SO2F2 (S is the central atom)
32 valence electrons
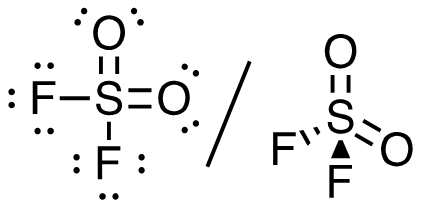
Answer: This molecule has a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry; sp3 hybridized (s + p + p + p)
5. XeO2F2 (Xe is the central atom)
34 valence electrons
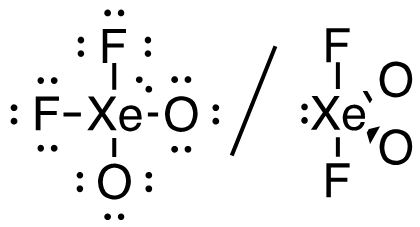
Answer: This molecule has a trigonal bipyramidal electron-pair geometry; sp3d hybridized (s + p + p + p + d)
Guided Solution
Do you want more help?
The guided solution below will give you the reasoning for each step to get your answer, with reminders and hints.
Show/Hide Guided Solution
| Guided Solution Ideas |
|---|
This question is a theory problem where you use your knowledge of molecular bonding and identify atomic orbital hybridization.
Show/Hide Resource
|
What is the pattern associated with atomic orbital hybridization?
Show/Hide Think About This!The hybridization of the centre atom will be determined by the electron-pair geometry, not the atom itself. For example, the centre atoms hybridization will always be sp in a linear molecule. Number of electron domains (as determined by the number of bonding directions and lone pairs in the best Lewis structure) = Number of atomic orbitals required for hybridization. Number of hybrid orbitals = Number of orbitals mixed. Hybrid orbitals are named by type and number of orbitals mixed. Show/Hide Don’t Forget!Recall the atomic orbitals: for n = 2 there is 1 ‘s’ orbital (l = 0) and 3 degenerate ‘p’ orbitals (l = 1). Note that ‘d’ orbitals (l = 2) can only exist when n is greater than or equal to 3.
|
| Complete Solution |
|---|
| a. CS2
16 valence electrons, C central atom
Answer: This molecule has a linear electron-pair geometry; sp hybridized (s + p) |
| b. Cl2CO (C is the central atom)
24 valence electrons
Answer: This molecule has a trigonal planar electron-pair geometry; sp2 hybridized (s + p + p) |
| c. Cl2SO (S is the central atom)
26 valence electrons
Answer: This molecule has a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry; sp3 hybridized (s + p + p + p) |
| d. SO2F2 (S is the central atom)
32 valence electrons
Answer: This molecule has a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry; sp3 hybridized (s + p + p + p) |
| e. XeO2F2 (Xe is the central atom)
34 valence electrons
Answer: This molecule has a trigonal bipyramidal electron-pair geometry; sp3d hybridized (s + p + p + p + d) |
Check Your Work
Verify that:
- Your Lewis structure has all the valence electrons.
- You have counted the central atom’s electron domains correctly.
The name of our electron pair geometry and number of electron domains leads us to the correct hybridization.
Does your answer make chemical sense?
Show/Hide Check Your Work!
Hybrid orbitals form due to the covalent bonding within molecules. When 2 or more atoms create a covalent bond, their atomic orbitals will overlap to form these hybrid orbitals.
In this case, we are looking at the hybridization of the centre atom to see what kind of hybridization is happening to overlap with all the atoms. When molecules grow and involve more atoms, more bonds form, and thus, more orbitals become involved. This is why a linear molecule only uses 2 orbitals (s + p), while an octahedral molecule uses 6 (s + p + p + p + d + d).
Provide feedback by taking the survey here: link to survey

PASS Attribution
- LibreTexts PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500 (4).
- Question 5.E.59 from LibreTexts PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500 (5) is used under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- Question 5.E.59 is question 8.E.1.1(b to f) from LibreTexts Chemistry 1e (OpenSTAX) (6), which is under a CC BY 4.0 license.
- Question 8.E.1.1(b to f) is question 27(b to f) from OpenStax Chemistry (7), which is under a CC BY 4.0 license. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/chemistry/pages/1-introduction.
References
1. OpenStax. 5.3: Hybrid Atomic Orbitals. In CHEM 1500: Chemical Bonding and Organic Chemistry; LibreTexts, 2022. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/CHEM1500:_Chemical_Bonding_and_Organic_Chemistry/05:_Chemical_Bonding_II-_Molecular_Geometry_and_Hybridization_of_Atomic_Orbitals/5.03:_Hybrid_Atomic_Orbitals.
2. OpenStax. 4.4: Lewis Symbols and Structures. In General Chemistry 1; LibreTexts, 2020. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Nassau_Community_College/General_Chemistry_1/04%3A_Chemical_Bonding_and_Molecular_Geometry/4.04%3A_Lewis_Symbols_and_Structures.
3. OpenStax. 5.1: Molecular Structure and Polarity. In CHEM 1500: Chemical Bonding and Organic Chemistry; LibreTexts, 2022. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/CHEM1500%3A_Chemical_Bonding_and_Organic_Chemistry/05%3A_Chemical_Bonding_II-_Molecular_Geometry_and_Hybridization_of_Atomic_Orbitals/5.01%3A_Molecular_Structure_and_Polarity.
4. Blackstock, L.; Brewer, S.; Jensen, A. PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500; LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/PASS_Chemistry_Book_CHEM_1500.
5. Blackstock, L.; Brewer, S.; Jensen, A. 5.3: Question 5.E.59 PASS – Identify Central Atom Hybridization. In PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500; LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/PASS_Chemistry_Book_CHEM_1500/05%3A_Chemical_Bonding_II_-_Molecular_Geometry_and_Hybridization_of_Atomic_Orbitals/5.03%3A_Question_5.E.59_PASS_-_identify_central_atom_hybridization.
6. OpenStax. 8.E: Advanced Theories of Covalent Bonding (Exercises). In Chemistry 1e (OpenSTAX); LibreTexts, 2022. https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/General_Chemistry/Chemistry_1e_(OpenSTAX)/08%3A_Advanced_Theories_of_Covalent_Bonding/8.E%3A_Advanced_Theories_of_Covalent_Bonding_(Exercises).
7. Flowers, P.; Robinson, W. R.; Langley, R.; Theopold, K. Ch. 8 Exercises. In Chemistry; OpenStax, 2015. https://openstax.org/books/chemistry/pages/8-exercises.

