Organic Chemistry — Bonding and Structure: Identifying Constitutional Isomers
You may choose to prevent this website from aggregating and analyzing the actions you take here. Doing so will protect your privacy, but will also prevent the owner from learning from your actions and creating a better experience for you and other users.
This opt out feature requires JavaScript.
Question
Indicate whether each of the following sets are constitutional isomers, the same compound, or different compounds.
-
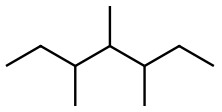
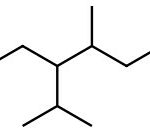
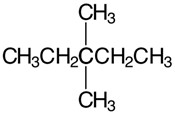
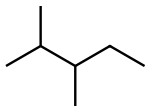
Set A -
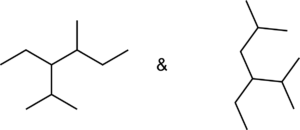
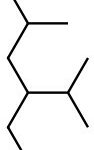
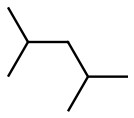
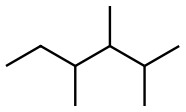
Set B -
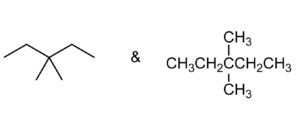
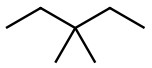
Set C -
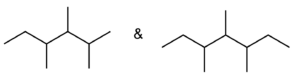
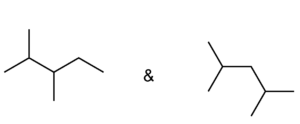
Set D
Show/Hide Answer
- Constitutional isomers
- Same compound
- Constitutional isomers
- Different compounds
Refer to Section 7.4: Alkanes and Alkane Isomers (1).
Strategy Map
Do you need a little help to get started?
Check out the strategy map.
Show/Hide Strategy Map
| Strategy Map Steps |
|---|
| 1. Identify the atoms that make up each compound (their chemical formula). |
| 2. Identify the connectivity of each compound. |
| 3. Compare the 2 compounds and identify what is the same/different between them. |
Solution
Do you want to see the steps to reach the answer?
Check out this solution.
Show/Hide Solution
a. Set A
Both structures have the same formula but different connectivity, which makes them constitutional isomers.
Answer: Constitutional isomers
b. Set B
Both structures have the same formula and connectivity, which makes them the same compound.
Answer: Same compound
c. Set C
Both structures have the same formula but different connectivity, which makes them constitutional isomers.
Answer: Constitutional isomers
d. Set D
Both structures have different formulas, which makes them different compounds.
Answer: Different compounds
Guided Solution
Do you want more help?
The guided solution below will give you the reasoning for each step to get your answer, with reminders and hints.
Show/Hide Guided Solution
| Guided Solution Ideas |
|---|
This question is a theory type problem where you must identify structural isomers based on their chemical formula and connectivity.
Show/Hide Resource
|
Recall what a constitutional isomer is.
Show/Hide Don’t Forget!Constitutional isomers are 2 or more molecules that have the same chemical formula (are composed of the same atoms) but different connectivity. For example, the methane group is attached to carbon 4 on one compound and carbon 6 on another, but both have the same chemical compounds. |
What will make the 2 compounds different compounds?
Show/Hide Think About This!Two compounds are considered different compounds if they have a different arrangement of atoms. |
| Complete Solution |
|---|
| a. Set A
Count the C and H atoms:
Answer: Constitutional isomers |
| b. Set B
Count the C and H atoms:
Answer: Same compound |
| c. Set C
Count the C and H atoms:
Answer: Constitutional isomers |
| d. Set D
Count the C and H atoms:
Answer: Different compounds |
Check Your Work
Reviewing your work above checking the connectivity and number of atoms will confirm your answers.
Does your answer make chemical sense?
Show/Hide Check Your Work!
The formula of compounds is determined by the atoms that compose them.
Multiple compounds can have the same chemical makeup and formula, but their connectivity may be different. If this is the case, they will be constitutional isomers. This differentiation is made because they will often have different chemical properties.
If the number of atoms and connectivity are the same, then they will be the same compound as in (b) where you are comparing a line structure drawing to a condensed structural formula. If the number of atoms is different as in (d), the molecular formula is different and they are different compounds.
Provide feedback by taking the survey here: link to survey

PASS Attribution
- LibreTexts PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500 (2).
- Question 7.4.6 from LibreTexts PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500 (3), which is used under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license.
- Question 7.4.6 is question 7.4.6 from LibreTexts CHEM 1500: Chemical Bonding and Organic Chemistry (1), which is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license.
- Question 7.4.6 is question 3.2.6 from LibreTexts Organic Chemistry (Morsch et al.) (4), which is under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license.
Media Attributions
All figures are by Ashlynn Jensen, from LibreTexts PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500 (3) by Blackstock et al., and are used/updated under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license.
References
1. Farmer, S.; Kennepohl, D.; Sharett, Z.; Morsch, L.; Cunningham, K.; Soderberg, T. 7.4: Alkanes and Alkane Isomers. In CHEM 1500: Chemical Bonding and Organic Chemistry; LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/CHEM_1500%3A_Chemical_Bonding_and_Organic_Chemistry/07%3A_Organic_Chemistry_I_-_Bonding_and_Structure/7.04%3A_Alkanes_and_Alkane_Isomers.
2. Blackstock, L.; Brewer, S.; Jensen, A. PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500; LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/PASS_Chemistry_Book_CHEM_1500.
3. Blackstock, L.; Brewer, S.; Jensen, A. 7.3: Question 7.4.6 PASS – Identifying Constitutional Isomers. In PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500; LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/PASS_Chemistry_Book_CHEM_1500/07%3A_Organic_Chemistry_I_-_Bonding_and_Structure/7.03%3A_Question_7.4.6_PASS_-_identifying_constitutional_isomers.
4. Farmer, S.; Kennepohl, D.; Sharrett, Z.; Morsch, L.; Cunningham, K.; Soderburg, T. 3.2: Alkanes and Alkane Isomers. In Organic Chemistry (Morsch et al.); LibreTexts, 2022. https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Organic_Chemistry/Organic_Chemistry_(Morsch_et_al.)/03%3A_Organic_Compounds-_Alkanes_and_Their_Stereochemistry/3.02%3A_Alkanes_and_Alkane_Isomers.

 &
& 
 &
& 
 &
& 
 &
&