Quantum Theory and Electronic Structure: Electron Configuration, Orbital Diagrams, Aufbau’s Principle, and Hund’s Rule
You may choose to prevent this website from aggregating and analyzing the actions you take here. Doing so will protect your privacy, but will also prevent the owner from learning from your actions and creating a better experience for you and other users.
This opt out feature requires JavaScript.
Question
Consider magnesium (Mg), silicon (Si), and sulfur (S). Which of the following atoms has 2 unpaired electrons?
- Mg
- Si
- S
- Both Mg and S
- Both Si and S
Show/Hide Answer
e. Both Si and S
Refer to Section 2.6: Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations) (1).
Strategy Map
Do you need a little help to get started?
Check out the strategy map.
Show/Hide Strategy Map
| Strategy Map Steps |
|---|
1. Find the element on the periodic table and note its atomic number.
Show/Hide HintThe atomic number (Z) describes the number of electrons the atom has.
Show/Hide ResourceRefer to Section 3.1: The Periodic Table (2). |
2. Create an orbital box diagram for each element’s electrons.
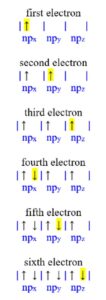
Show/Hide HintOrbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration; it shows the individual orbitals as boxes and the pairing arrangement of electrons as arrows. Begin to fill your box orbital diagram starting with the lowest energy ‘1s’ orbital, and stop when you “run out” of electrons. Follow Hund’s Rule and Aufbau’s Principle. When filling degenerate (same energy) orbitals, Hund’s Rule must be obeyed to maintain the most stable (lowest energy) electron configuration. Hund’s Rule is shown below:
|
3. Count the number of unpaired electrons.
Show/Hide HintAny orbitals containing 1 single electron are described as unpaired electrons. |
Solution
Do you want to see the steps to reach the answer?
Check out this solution.
Show/Hide Solution
Magnesium (Mg)
z = 12; 12 electrons
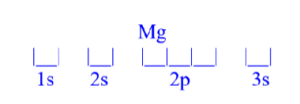
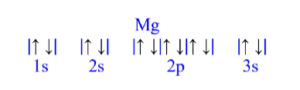
Mg has 0 unpaired electrons.
Silicon (Si)
z = 14; 14 electrons
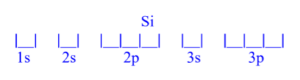
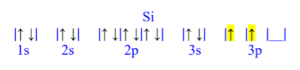
Silicon has 2 unpaired electrons.
Sulfur (S)
z = 16; 16 electrons
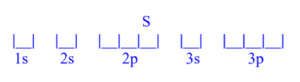

Sulfur has 2 unpaired electrons.
Answer: Both Si and S
Guided Solution
Do you want more help?
The guided solution below will give you the reasoning for each step to get your answer, with reminders and hints.
Show/Hide Guided Solution
| Guided Solution Ideas |
|---|
This question relies on concepts on the electronic structure of atoms.
Show/Hide Resource
|
| What does the question ask you to find?
Question: “Consider magnesium (Mg), silicon (Si), and sulfur (S). Which of the following atoms has 2 unpaired electrons?” Consider the circumstances in which electrons are paired or unpaired. Show/Hide Don’t Forget!
|
How many electrons does each element have?
Show/Hide Don’t Forget!
|
| Complete a box orbital diagram to determine the number of unpaired electrons for each element:
Show/Hide Watch Out!
|
| Fill the appropriate number of electrons into each box diagram:
Show/Hide Don’t Forget!Add electrons from left to right:
Refer to Example 2.6.1: Quantum Numbers and Electron Configurations in Section 2.6 (1) |
| Complete Solution |
|---|
| Magnesium (Mg) is atomic number 12 and has a total of 12 electrons. The diagram is filled starting with a pair of electrons in the 1s orbital box, followed by 2s, the 2p then 3s.
All electrons are paired in magnesium.
Silicon (Si) is atomic number 14 and has a total of 14 electrons. The diagram is filled starting with the 1s orbital box, followed by 2s, 2p, 3s then 3p. The 3p orbital has 2/6 electrons, meaning silicon has 2 unpaired electrons.
Sulfur (S) is atomic number 16 and has a total of 16 electrons. The diagram is filled starting with the 1s orbital box, followed by 2s, 2p, 3s then 3p. The 3p orbital has 4/6 electrons, meaning sulfur has 2 unpaired electrons.
Answer: Both Si and S have 2 unpaired electrons |
Check Your Work
Summary of what we would expect based on the related chemistry theory.
Show/Hide Check Your Work!
Be sure that your box orbital diagram adheres to the guidelines:
- The lowest energy available orbitals should be filled first.
- Box orbitals on the left are lower energy than the right (Aufbau’s Principle).
- All paired arrows should have opposite spin (Pauli’s Exclusion Principle).
- When same energy orbitals are available (3 ‘p’ orbitals, or 5 ‘d’ orbitals), electrons remain unpaired with the same spin until no unoccupied orbitals remain (Hund’s Rule).
Does your answer make chemical sense?
Show/Hide Answer
When completing the box orbital diagram, count the number of arrows representing electrons; be sure it matches the number of electrons determined from the atomic number (z)!
Provide feedback by taking the survey here: link to survey

PASS Attribution
- LibreTexts PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500 (3).
- Question 2.E.58 from LibreTexts PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500 (4) is used under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- Question 2.E.58 was adapted from question 6.4.13 from LibreTexts Chemistry 1e (OpenSTAX) (5), which is under a CC BY 4.0 license.
- Question 6.1.6 is question 59 from OpenStax Chemistry 2e (6), which is under a CC BY 4.0 license. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/chemistry-2e/pages/1-introduction.
Media Attributions
Unless otherwise noted, all figures by the authors (Brewer S. and Blackstock L.) are free to use under a CC0 license.
- Periodic Table of Elements Black and White [adapted from Dmarcus100] by Thompson Rivers University Open Learning (7) is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license.
References
1. OpenStax. 2.6: Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations). In CHEM1500: Chemical Bonding and Organic Chemistry. LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/CHEM_1500%3A_Chemical_Bonding_and_Organic_Chemistry/02%3A_Quantum_Theory_and_Electronic_Structure_of_Atoms/2.06%3A_Electronic_Structure_of_Atoms_(Electron_Configurations).
2. OpenStax. 3.1 The Periodic Table. In CHEM1500: Chemical Bonding and Organic Chemistry. LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/CHEM_1500%3A_Chemical_Bonding_and_Organic_Chemistry/03%3A_Periodic_Relationships_Among_the_Elements/3.01%3A_The_Periodic_Table.
3. Blackstock, L.; Brewer, S.; Jensen, A. PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500; LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/PASS_Chemistry_Book_CHEM_1510%2F%2F1520.
4. Blackstock, L.; Brewer, S.; Jensen, A. 2.4: Question 2.E.58 PASS – Electron Configuration, Orbital Diagrams, Aufbau’s Principle Hund’s Rule. In PASS Chemistry Book CHEM 1500. LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Thompson_Rivers_University/PASS_Chemistry_Book_CHEM_1500/02%3A_Quantum_Theory_and_Electronic_Structure/2.04%3A_Question_2.E.58_PASS_-_electron_configuration_orbital_diagrams_Aufbau’s_Principle_Hund’s_Rule.
5. OpenStax. 6.E: Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties (Exercises). In Chemistry 1e (OpenSTAX). LibreTexts, 2023. https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/General_Chemistry/Chemistry_1e_(OpenSTAX).
6. Flowers, P.; Robinson, W. R.; Langley, R.; Theopold, K. Ch. 6 Exercises. In Chemistry 2e; OpenStax, 2019. https://openstax.org/books/chemistry-2e/pages/6-exercises.
7. Thompson Rivers University Open Learning. Periodic Table Of Elements Black And White [adapted from Dmarcus100].